Ice cream: the quintessential summertime treat. It’s creamy, refreshing, and undeniably delicious. But behind that delightful taste lurks a potential downside: harmful health risks associated with excessive consumption of ice cream. While the occasional scoop won’t do much harm, indulging in a daily pint can wreak havoc on your health.
This article explores the harmful health risks of eating ice cream, providing valuable insights to help you make informed choices about this popular dessert. We’ll also discuss healthier alternatives to satisfy your sweet tooth without compromising your well-being.
Unveiling the Unhealthy Side of Ice Cream: A Breakdown of Key Concerns

Ice cream is typically high in:
- Fat: Full-fat ice cream can be loaded with saturated fat, a major contributor to heart disease, the leading cause of death globally. According to the American Heart Association, limiting saturated fat intake to less than 5-6% of your daily calories is recommended.
- Sugar: Many ice creams boast sky-high sugar content. Excessive sugar consumption is linked to a multitude of health problems, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and even certain cancers.
- Calories: A single serving of ice cream can easily pack hundreds of calories. Regularly exceeding your daily calorie needs can lead to weight gain and associated health risks.
- Dairy: For those with lactose intolerance, ice cream can trigger digestive issues like bloating, gas, and diarrhea.
Let’s delve deeper into some specific harmful health risks associated with overconsumption of ice cream:
- Weight Gain and Obesity: The combination of high fat, sugar, and calories in ice cream can significantly contribute to weight gain. Obesity is a major risk factor for various health problems, including heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes.
- Increased Risk of Heart Disease: Saturated fat in ice cream can raise LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels, while hindering HDL (“good”) cholesterol. This imbalance increases the risk of plaque buildup in arteries, leading to heart disease and stroke.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Excessive sugar intake can overwhelm your body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels, potentially leading to type 2 diabetes. Research suggests a strong link between high sugar intake and increased risk of developing diabetes.
- Dental Problems: The high sugar content in ice cream can contribute to tooth decay and cavities, especially with frequent consumption.
Here are some statistics to illustrate the impact of excessive sugar intake:
- The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends limiting added sugar intake to no more than 10% of your daily calorie intake, ideally less than 5%.
- According to the American Heart Association, the maximum recommended daily added sugar intake for women is 25 grams and for men is 36 grams.
It’s important to remember that these risks are primarily associated with excessive ice cream consumption.
Finding Balance: Enjoying Ice Cream in Moderation
Does this mean you have to swear off ice cream forever? Absolutely not! The key lies in moderation. Here are some tips to enjoy ice cream without jeopardizing your health:
- Portion Control: Stick to smaller portions. Opt for a kid’s size cone or share a pint with a friend.
- Frequency: Limit ice cream consumption to occasional treats, not a daily habit.
- Choose Lower-Fat Options: Many brands offer delicious lower-fat or frozen yogurt alternatives.
- Homemade Goodness: Consider making your own ice cream with healthier ingredients like fruits and natural sweeteners.
- Pair it with Fruit: Top your ice cream with fresh berries or sliced banana for added nutrients and fiber.
Beyond Moderation: Exploring Alternatives and Addressing Specific Concerns
While moderation is key, some individuals might have specific health conditions or dietary restrictions that necessitate a complete avoidance of ice cream. Here’s how to navigate those situations:
- Lactose Intolerance: Many brands offer lactose-free ice cream alternatives made with almond milk, coconut milk, or soy milk. These options allow those with lactose intolerance to enjoy a similar frozen treat without digestive discomfort.
- Vegan Diet: Vegan ice cream options are readily available, often made with coconut milk or cashews. These alternatives provide a creamy and delicious treat that aligns with a vegan lifestyle.
- Diabetic Concerns: Sugar-free ice creams sweetened with alternative sweeteners like stevia or erythritol can be an option for those with diabetes. However, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before including these products in your diet.
It’s important to note that sugar-free ice cream might still contain high amounts of fat and calories, so moderation is still important.
Addressing Specific Concerns: A Deeper Dive
Let’s address some of the points you raised in your original article and provide a more nuanced perspective:
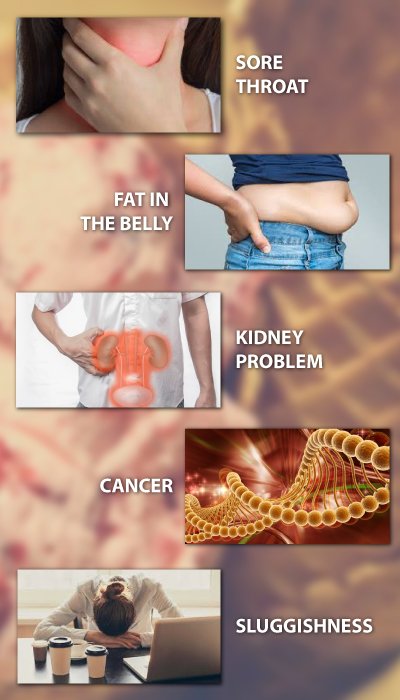
- Kidney Problems: While there isn’t a direct link between moderate ice cream consumption and kidney problems, the high sugar content could indirectly contribute to health issues that can put a strain on the kidneys in the long run, like obesity or diabetes.
- Cancer: There’s no scientific evidence to suggest that ice cream directly causes cancer. However, some commercially produced ice creams might contain artificial flavors or colorings that have raised concerns in some studies. Opting for natural ingredients and avoiding heavily processed ice cream varieties can help minimize any potential risks.
- Sore Throat and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): While the coldness of ice cream might aggravate a sore throat or cough temporarily, it’s not a long-term health risk. For individuals with COPD, managing their condition through medication and avoiding irritants like smoke is the primary focus. Ice cream itself isn’t necessarily a trigger, but very cold foods might cause some discomfort. Consulting with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance is recommended.
Remember, a balanced diet with a variety of foods is essential for maintaining good health. Ice cream can be a part of that balanced diet, but it’s important to be mindful of portion sizes and frequency of consumption.
Conclusion: Making Informed Choices About Ice Cream
Ice cream, when enjoyed in moderation, can be a delightful treat. By understanding the harmful health risks associated with overindulgence and making informed choices, you can strike a healthy balance and savor this summertime favorite without compromising your well-being. Explore healthier alternatives, prioritize portion control, and opt for lower-fat or lower-sugar varieties whenever possible. Remember, a balanced and mindful approach to ice cream consumption allows you to enjoy its refreshing taste without sacrificing your health goals.
